A push notification may look like a simple popup on a user’s screen, but delivering that message at the right time, to the right device, under unpredictable network conditions is a surprisingly complex problem.
Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) exists to solve exactly this challenge. It provides a reliable communication layer between backend systems and user devices, without forcing developers to manage low-level delivery infrastructure.
What Is Firebase Cloud Messaging?
Firebase Cloud Messaging is a cloud-based messaging service by Google that enables servers to send messages to client applications such as mobile apps, web apps, and background services.
While it is commonly used for push notifications, FCM is fundamentally a message delivery system, not just a notification tool.
Core Idea
Your backend sends a message once — FCM ensures it reaches the correct device, even if the app is offline or running in the background.
The Problem FCM Is Designed to Solve
Building your own push system means handling persistent connections, retries, offline devices, throttling, and platform-specific rules.
- Mobile devices constantly change network state
- Apps are frequently backgrounded or killed
- Each platform enforces different delivery constraints
- Scaling to millions of devices is non-trivial
FCM abstracts these problems behind a single, unified messaging API.
High-Level FCM Architecture
Conceptually, FCM acts as an intelligent intermediary between your backend infrastructure and user devices.
- Your backend server (message producer)
- Firebase Cloud Messaging (delivery broker)
- User devices (message consumers)
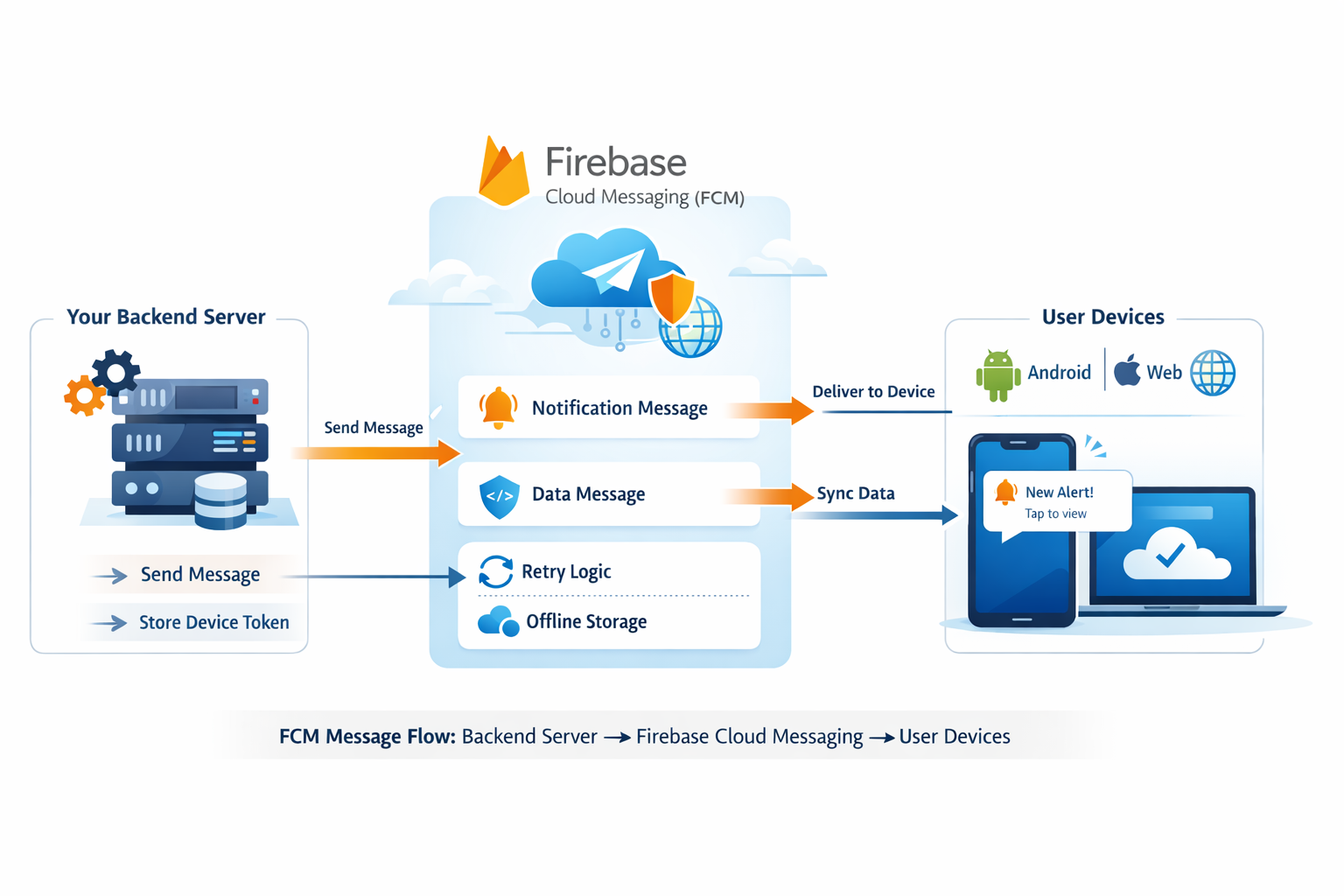
FCM Message Flow: Backend Server → Firebase Cloud Messaging → User Devices
Each app instance registered with Firebase receives a unique registration token, which identifies exactly where messages should be delivered.
Message Delivery Lifecycle
When an app is installed and initialized, Firebase generates a device-specific token. This token may change over time and must be kept updated by your backend.
- App initializes Firebase SDK
- FCM issues a unique registration token
- Backend securely stores the token
- Backend sends a message request to FCM
- FCM routes the message to the target device
If the device is offline, FCM stores the message temporarily and retries delivery when the device reconnects.
Notification Messages vs Data Messages
FCM supports different types of messages depending on how the app should react.
- Notification messages: Display UI notifications automatically
- Data messages: Deliver raw data for background processing
This flexibility allows FCM to function as both a user-facing notification system and a silent background communication channel.
Why FCM Scales So Well
FCM benefits directly from Google’s global infrastructure, which handles load balancing, retries, authentication, and regional routing automatically.
- Low-latency global delivery
- Automatic retry and failover
- Secure server authentication
- No server maintenance overhead
FCM Is Not a Real-Time Socket
It is important to understand that FCM is not designed to replace WebSockets or persistent real-time connections.
Instead, it is optimized for reliable, event-driven message delivery, making it ideal for notifications, alerts, and background sync triggers.
Think of FCM as a highly reliable postal system, not a live phone call.
Key Takeaways
- FCM abstracts complex push delivery infrastructure
- It works across platforms and device states
- It supports both visible and silent messages
- It scales from small apps to millions of users
Final Thoughts
Firebase Cloud Messaging allows developers to focus on application logic instead of worrying about delivery reliability and scale.
By acting as a robust messaging backbone, FCM plays a critical role in modern mobile and web application architectures.
← Back to Blogs